데이터 집계를 위한 배치 처리 시
GROUP BY와SUM대신 Redis를 활용하여 성능을 대폭 개선할 수 있는 방법에 대해 알아봅시다!
🚀 들어가기
대용량 데이터의 집계 처리는 배치 애플리케이션에서 자주 발생하는 작업이지만, 처리해야 할 데이터 양이 증가할수록 성능 이슈가 발생합니다. 본 포스트에서는 기존 GROUP BY, SUM 등 SQL 기반 집계 대신 Redis를 활용한 고성능 집계 방법과 그 최적화 과정에 대해 단계별로 알아보겠습니다.
기존 GROUP BY, SUM 쿼리의 한계
통계 처리 시 일반적으로 GROUP BY, SUM 쿼리를 사용하는 것은 데이터가 적을 때는 효율적입니다. 그러나 데이터가 대용량으로 증가하고 쿼리가 복잡해질수록 여러 성능 문제가 발생합니다:
- 여러 테이블을
JOIN하고GROUP BY하는 복잡한 쿼리는 데이터베이스 옵티마이저가 비효율적인 실행 계획을 생성할 수 있습니다. - 대량의 데이터 처리 과정에서 임시 테이블 생성으로 인한 디스크 I/O 부하가 증가합니다.
- 데이터 양이 증가할수록 쿼리 실행 시간이 기하급수적으로 증가합니다.
- 쿼리 튜닝이 복잡해지고 데이터베이스 리소스 사용량이 급증합니다.
아래 코드는 배치 과정에서 정산 데이터를 집계하기 위해 GROUP BY, SUM을 사용한 SQL문 입니다:
1 | |
Redis를 활용한 효율적인 집계 처리
대용량 데이터 집계 시 발생하는 GROUP BY 쿼리의 문제를 해결하기 위해 집계 연산을 디스크 기반 RDB 데이터베이스가 아닌 인메모리 데이터베이스인 Redis로 이관할 수 있습니다.
Redis를 집계 처리에 활용하면 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다:
- 집계에 최적화된 연산 API 지원 (
hincrby,hincrbyfloat등) - 메모리 기반 처리로 디스크 I/O 병목 현상 제거
- 인메모리 데이터베이스의 초고속 연산 처리 능력
🚨 주의사항:
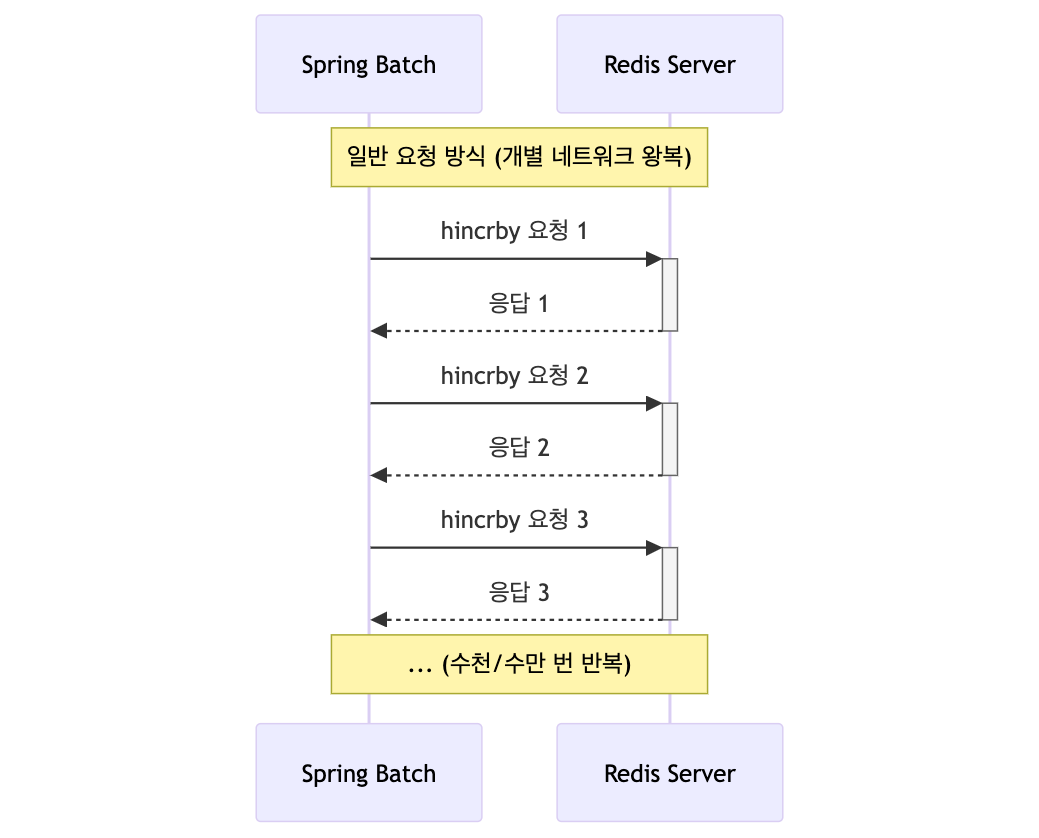
Redis를 사용하면 집계 연산을 빠르게 처리할 순 있지만, 병목 지점이 될 수 있는 지점이 네트워크 레이턴시입니다. 1,000만 개의 데이터를 합산하기 위해 1,000만 번의 개별 네트워크 요청이 발생한다면, 이로 인한 성능 저하는 피할 수 없습니다. ☠️
Redis Pipeline을 통한 네트워크 레이턴시 최소화
Redis Pipeline을 활용하면 수많은 Redis 명령을 묶어서 한 번의 네트워크 왕복으로 처리할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 1,000만 번의 개별 네트워크 요청을 청크 단위로 묶어 1만 번 정도로 줄이면 집계 처리 시간을 획기적으로 단축할 수 있습니다.
개별 요청 방식
Pipeline 방식

💡 중요한 구현 포인트:
Spring Batch의 청크 프로세싱 아키텍처를 고려할 때, Redis 파이프라인은 반드시 ItemWriter에서 생성해야 합니다. Spring Batch는 ItemReader → ItemProcessor 단계에서는 항목을 하나씩 처리하다가, 지정된 Chunk 크기만큼 항목이 처리되면 ItemWriter에게 묶음으로 전달합니다.
만약 ItemProcessor에서 Redis Pipeline을 생성한다면, 항목마다 Redis 연결을 맺고 끊는 불필요한 오버헤드가 발생합니다. 따라서 ItemWriter에서 청크 단위로 파이프라인을 처리하는 것이 최적의 구현 방식입니다.
(처음에 청크 프로세싱 아키텍처를 고려하지 않고, 단순히 ItemProcessor에서 처리하는게 자연스럽단 착각 덕분에 성능이 나빠진 제 경험으로부터 알려드립니다. 😂)
다음은 정산 데이터(settlement_detail) 청크를 정산 항목별로 Redis에서 파이프라인을 사용해 집계 처리하는 코드입니다:
1 | |
이 방식을 적용한 후에도 redisAsyncCommands 클라이언트를 통해 반복되는 연산 요청을 매번 파이프라인에 적재해야 하므로, 기존 GROUP BY 대비 성능 개선이 기대보다 크지 않았습니다.
더 높은 성능 개선을 위해 구글링과 AI에게 조언을 구하여, 저수준 API 활용 방법 중 Lua 스크립트 사용을 고려해 보게 되었습니다.
Lua 스크립트를 활용한 집계 처리
파이프라인에 연산 명령어를 적재하는 과정에서도 여전히 애플리케이션 측에서 많은 연산 로직이 필요하다는 사실을 발견했습니다.
(🤔 StepListener를 활용하여 명령어를 적재하는 과정이 얼마나 시간이 걸리는지 측정했습니다.)
이를 해결하기 위해 Lua 스크립트를 활용하여 데이터만 Redis 서버로 전송하고, 모든 집계 연산은 Redis 서버에서 직접 수행하도록 개선했습니다.
이 접근 방식의 핵심 장점은 다음과 같습니다:
- 애플리케이션 측의 연산 오버헤드 제거
- 데이터 전송량 최소화
- Redis 서버에서의 원자적 실행 보장
- 복잡한 로직을 단일 스크립트로 캡슐화
다음은 정산 집계를 위한 Lua 스크립트입니다:
1 | |
다음은 Lua 스크립트를 활용해 Redis에서 집계 연산을 수행하는 ItemWriter 구현입니다:
1 | |
Lua 스크립트 사용 시 주의사항과 트레이드 오프
Lua 스크립트를 통한 최적화는 큰 성능 향상을 가져올 수 있지만, 몇 가지 중요한 고려사항과 트레이드 오프가 존재합니다:
📌 Redis 서버 부하 증가:
- 집계 연산의 부하가 애플리케이션에서 Redis 서버로 이동합니다.
- 복잡한 스크립트는 Redis의 싱글 스레드 특성으로 인해 다른 작업을 차단할 수 있습니다.
- 특히 고부하 상황에서 Redis 서버의 CPU 사용률을 모니터링해야 합니다.
📌 디버깅 복잡성:
- Lua 스크립트 내부에서 발생하는 오류는 디버깅이 어렵습니다.
- 로그 출력 등 디버깅 정보를 얻기 어려우므로 철저한 테스트가 필요합니다.
- 스크립트 오류 시 전체 트랜잭션이 실패할 수 있어 롤백 전략이 필요합니다.
📌 유지보수 복잡성:
- Lua 스크립트에 대한 버전 관리와 배포 전략이 필요합니다.
📌 Lua 언어 학습 곡선:
- 개발팀이 Lua 언어에 익숙하지 않을 경우 추가적인 학습 비용이 발생합니다.
📌 원자성 제한:
- Lua 스크립트는 단일 Redis 인스턴스에서는 원자적이지만, 클러스터 환경에서는 원자성이 보장되지 않습니다.
- 클러스터에서 여러 키에 걸친 작업을 수행할 때는 모든 키가 동일한 슬롯에 있어야 합니다.
📌 메모리 사용량 증가:
- Lua 스크립트 실행 중 생성되는 임시 데이터는 Redis 메모리를 사용합니다.
- 대규모 데이터 처리 시
maxmemory설정과 메모리 모니터링이 중요합니다.
이러한 트레이드 오프를 고려하여, 다음과 같은 상황에서 Lua 스크립트 사용을 권장합니다:
- 집계, 카운팅 등 단순하고 반복적인 연산이 필요한 경우
- 네트워크 왕복을 최소화해야 하는 성능 매우 중요한 상황
- Redis 서버의 리소스가 충분한 경우
반면, 다음과 같은 경우는 파이프라인이나 다른 방식을 고려해 볼 수 있습니다:
- 로직이 매우 복잡하고 자주 변경되는 경우
- Redis 클러스터 환경에서 여러 키를 사용해야 하는 경우
- Redis 서버가 이미 높은 부하를 겪고 있는 경우
성능 비교 및 결론
세 가지 구현 방식의 성능을 비교한 결과는 다음과 같습니다:
- 처리 속도 향상:
GROUP BY쿼리 대신 레디스hincrby연산으로 처리 속도 향상 - 데이터베이스 부하 감소: 데이터베이스의 집계 연산 부담 제거
- 확장성 향상: 데이터 증가에도 선형적인 성능 유지
- 실시간 집계 가능: 배치 작업과 실시간 집계를 병행 가능
결론
대용량 데이터 집계가 필요한 Spring Batch 애플리케이션에서는 단순히 SQL의 GROUP BY에 의존하기보다 Redis와 같은 인메모리 데이터베이스를 활용하고, Lua 스크립트를 통한 서버 사이드 처리를 구현하여 최적의 성능을 얻을 수도 있습니다. 본 포스트가 배치 처리의 성능을 높이는 데 도움이 되었으면 좋겠습니다.
감사합니다.
참고 자료
- Batch Performance 극한으로 끌어올리기: 1억 건 데이터 처리를 위한 노력 / if(kakao)dev2022
- Spring Batch 애플리케이션 성능 향상을 위한 주요 팁 (kakao tech)
- Redis Commands Docs - hincrby
- Redis Commands Docs - hincrbyfloat
- Redis Docs - Scripting with Lua